Types of counselling
- F2F
- Online
- Phone counselling session between F2F or between Online sessions
For who?
- Teenagers and young adults
- Adults
- Couple
- Family
- Group
- LGBTQIA+
- Locals and expatriates
Issues
Depression, Self-harm, Anxiety, Burnout, Grief, Expatriates’ issues, Teenagers’ issues, Relationship, Mid-Life crisis, Couple’s issues, Workplace issues, Trauma
Anger, Crisis response,
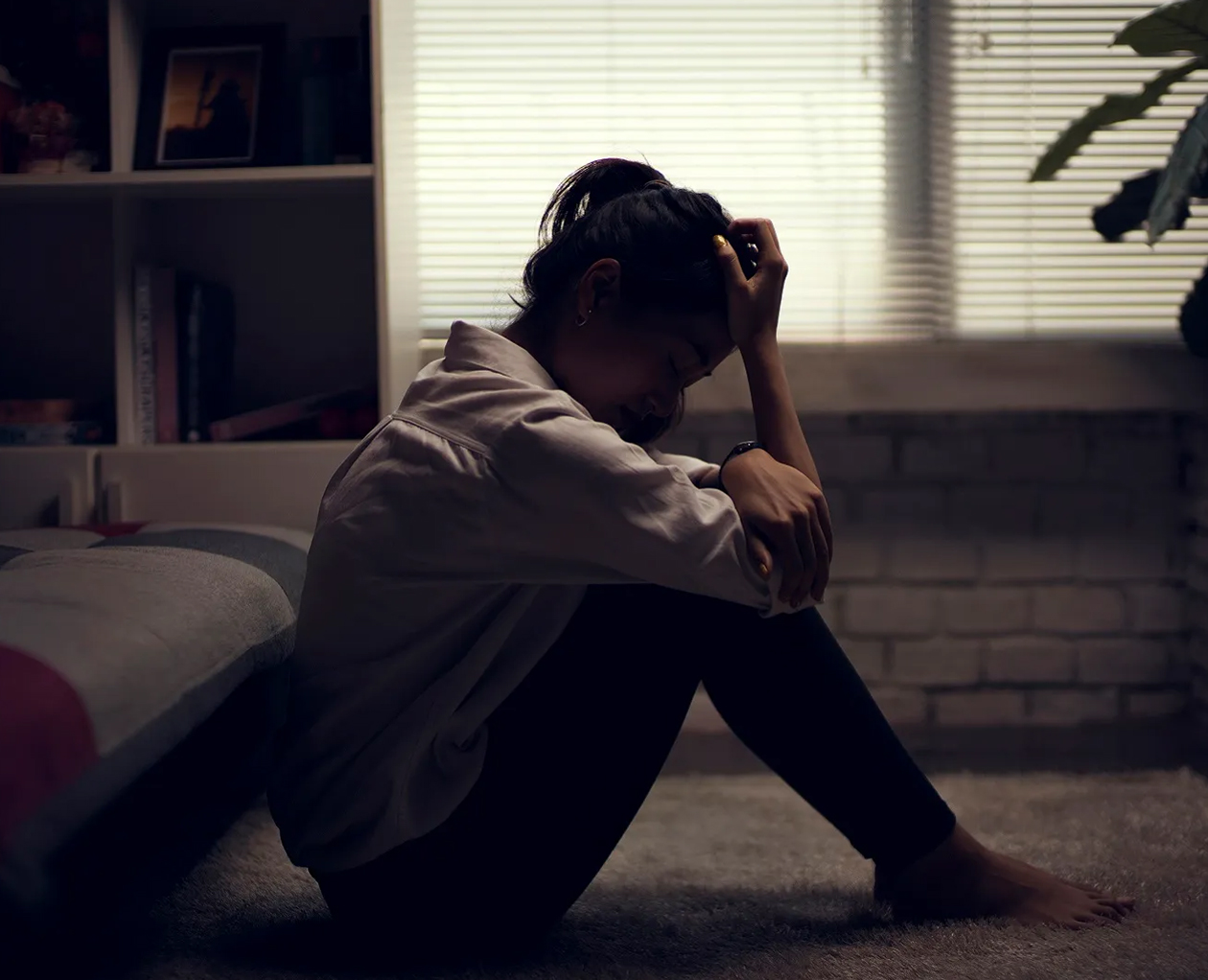

Depression
Depression is different from feeling low
It is a mental health condition that can cause a range of intense and persistent feelings. These can include a sense of sadness or emptiness, a loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyed, and feelings of hopelessness or worthlessness. Depression can also cause physical symptoms such as fatigue, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and difficulty concentrating. People with depression may feel irritable or agitated, experience a loss of motivation, and have thoughts of self-harm or suicide. These feelings can be overwhelming and make it challenging to carry out daily tasks or maintain relationships.
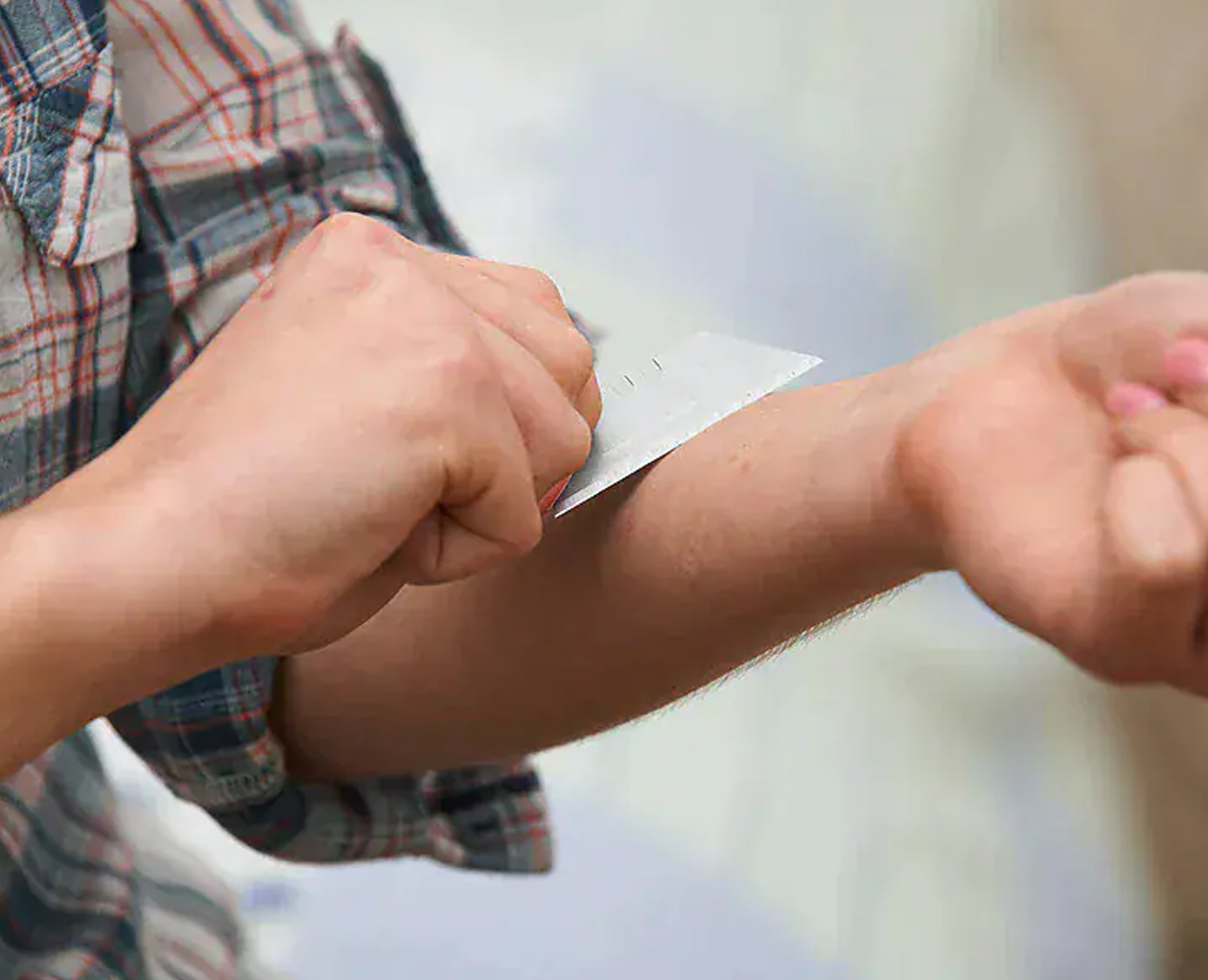
Self-harm
Self-harm can take many forms, including cutting, burning, scratching, overdosing on medication, or hitting oneself.
A person who engages in self-harm behaviour intentionally harms themselves as a way to cope with emotional pain or distress or to punish themselves if they think they have done something wrong, or even to make others aware of how they feel
Self-harm may lead to a sense of relief or release from emotional pain in the short term, but it can lead to further physical and emotional harm in the long term. Besides, there may be a risk of accidental suicide through self-harm
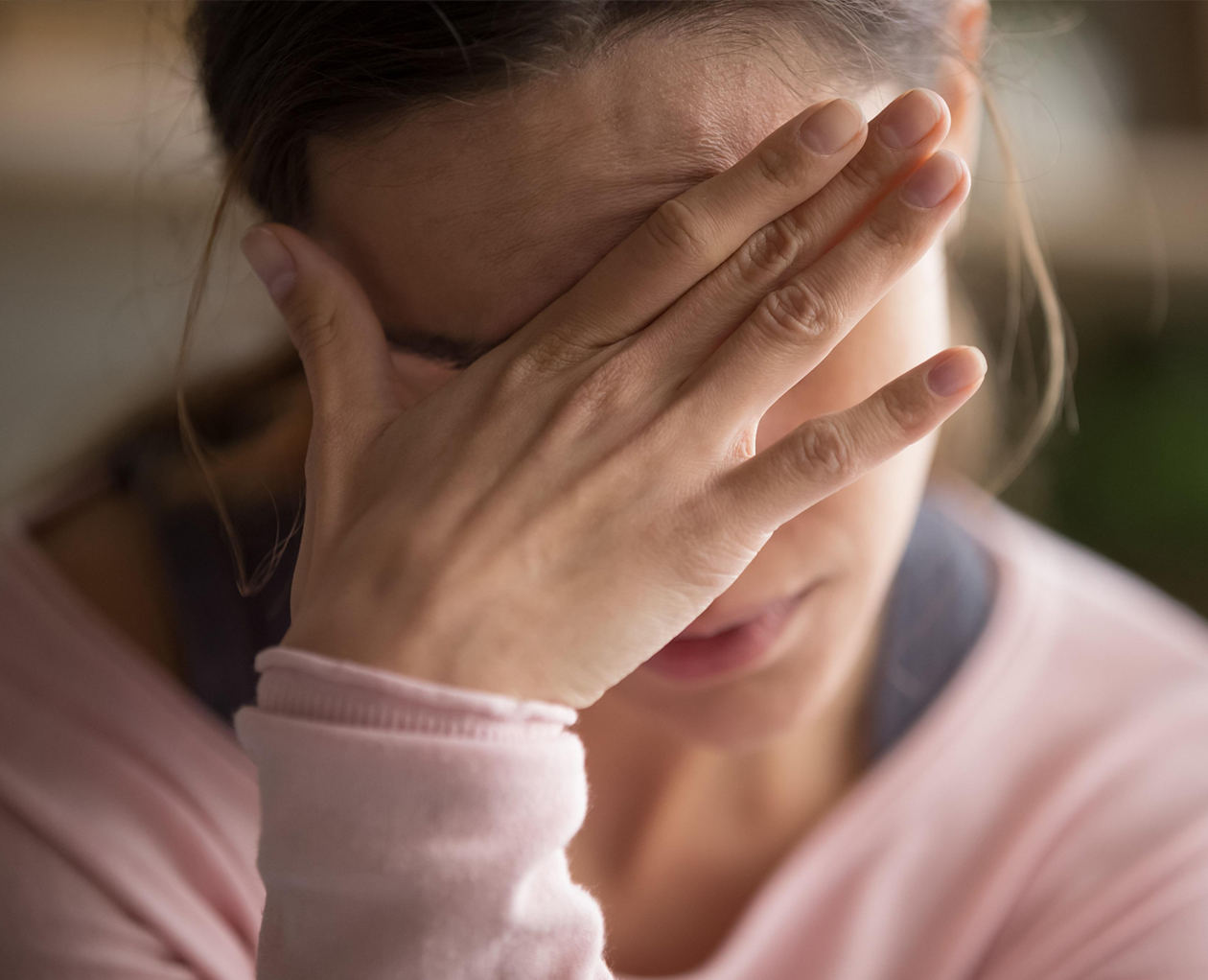


Anxiety
Anxiety is the intense and persistent feelings of worry or fear. People with anxiety may feel a sense of distress or uneasiness before a significant event. They may also experience physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and shortness of breath. Anxiety can cause individuals to avoid certain situations or activities, leading to social isolation or difficulty carrying out daily tasks. In some cases, anxiety can also lead to panic attacks, which involve sudden and intense feelings of fear or discomfort.
While a certain level of Anxiety helps us stay alert, a person suffering from an anxiety disorder, feels completely overwhelmed and dreads certain daily activities
Burnout
Burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by prolonged exposure to stress or pressure. Burnout is not only related to work situations but can also in other areas of life, such as romance, parenting, taking care of a loved one.
A person with burnout may feel overwhelmed, emotionally drained, and unable to meet the demands of their work or personal life. They may experience a lack of motivation or a sense of disillusionment with their work or relationships. Burnout can also cause physical symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, and muscle pain. If left untreated, burnout may lead to further negative consequences on overall health and well-being.


Grief
Grief is a natural response to loss, and a person who is grief-stricken experiences intense feelings of sadness, despair, and pain due to a significant loss. This loss can be the death of a loved one, the end of a relationship, or a major life change. A person experiencing grief feels a range of emotions such as anger, guilt, anxiety, loneliness, and confusion. They may also experience physical symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, insomnia, and loss of appetite
Expatriate’s adjustment
Changing country and adjusting to a new culture can be fun to some expatriates. To others, it may be challenging as they may face a range of issues linked to adjusting to a new way of life. These can include language barriers, cultural differences, and homesickness. They may struggle to build relationships and social networks in a new environment, which can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness. Additionally, expatriates may experience stress and anxiety related to their job responsibilities and the pressure to succeed in a new environment.


Teenage issues
Being a teenager is never an smooth journey. Most of the time, teenagers face a range of issues that can impact their mental health and wellbeing. These include academic pressure, social media and peer pressure, bullying, family conflict, and mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. These issues can lead to feelings of isolation, low self-esteem, and hopelessness.
Marital/ Couple’s issues
Marital issues are problems that arise in a marriage or long-term committed relationship. These issues can range from minor disagreements to more significant problems that can threaten the stability of the relationship. Common marital issues include communication problems, financial difficulties, infidelity, sexual issues, emotional unavailability, and differences in values or priorities. Marital issues can lead to feelings of frustration, anger, and sadness, and can have negative consequences for both partners and any children involved.


Mid-life Crisis
Midlife crisis is a period of self-doubt and questioning that can occur in people during their 40s or 50s. It is a time when individuals may reflect on their life choices and feel a sense of dissatisfaction or unfulfillment. They may experience a desire for change or a need to reassess their priorities and goals. Midlife crisis can be triggered by a variety of factors, such as career changes, health issues, loveless romantic relationship,or the death of a loved one. Symptoms of midlife crisis can include anxiety, depression, a sense of restlessness or boredom, and a sense of being lost.
Work place issues
Workplace issues refer to any problems or challenges that arise in a work environment and that affect employees' well-being, productivity, or job satisfaction.
These issues can include conflicts with co-workers or managers, discrimination, harassment, safety concerns, inadequate compensation or benefits, lack of opportunities for growth or advancement, schedule inflexibility, and more.
Addressing workplace issues is important for creating a positive work culture and ensuring the success of both employees and the organization.


Trauma
Trauma is a person’s emotional response to a distressing experience. It can be caused by a wide range of events. Traumatic events tend to be sudden and unpredictable, and feel beyond a person’s control.
Disturbing events activate the amygdala, a structure in the brain responsible for detecting threats. It responds by sending out an alarm to multiple body systems to prepare for defense. A normal response to trauma would be fear, anxiety, shock, anger or even aggression. They usually dissipate with time, however for some people, the distressing feelings can linger, interfering with day-to-day life.
Trauma can cause feelings of fear, helplessness, and a loss of control, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, depression, flashbacks, and nightmares. Trauma can be acute, complex or secondary. It can also result of adverse childhood experiences
Trauma affects an individual's ability to form and maintain relationships, work, and engage in daily activities if left untreated